Describe the Reaction Mechanism Using Two or Less Sentences
When everything happens simultaneously it is called a concerted mechanism. The negatively charged carbon belonging to the ylide is nucleophilic.

Mcb Exam 4 Sapling Flashcards Quizlet
Fe O 2 H 2 O Fe 2 O 3.
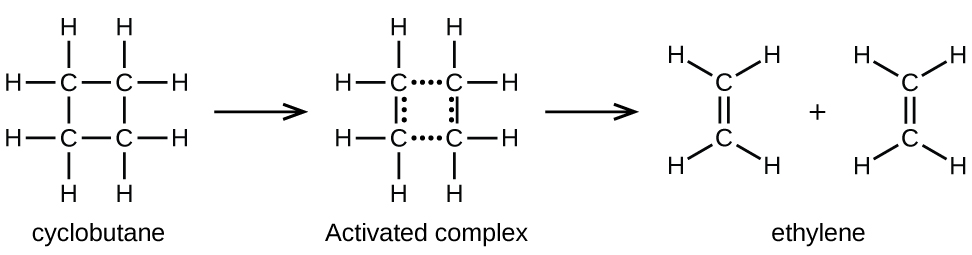
. A reaction that occurs in two or more elementary steps is called a multistep or complex reaction. Each of these events constitutes an elementary step that can be represented as a coming-together of discrete particles collison or as the breaking-up of a molecule dissociation into simpler units. A reaction mechanism is the sequence of elementary steps by which a chemical reaction occurs.
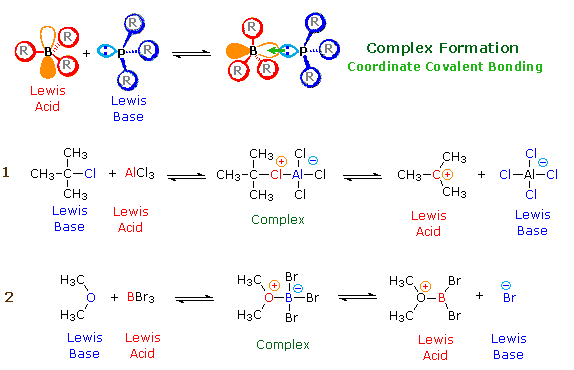
I need to describe the reaction mechanism using two or less sentences per each step of the mechanism. A reaction intermediate is a chemical species that is formed in one elementary step and consumed in a subsequent step. The Lewis acid catalyst AlCl 3 undergoes reaction with the alkyl halide resulting in the formation of an electrophilic carbocation.
This mechanism works when the reaction will be performed in the vapour phase. This form suggests that the rate-determining step is a reaction between two molecules of NO 2. Reaction mechanisms can agree with experimental data but can never be proven for certain.
Bonds are broken and new ones formed that happen to result in the initial reactants. This carbon proceeds to execute a nucleophilic attack on the carbonyl carbon of the aldehyde or ketone. If the reaction were to take place by the collisions of two N 2 O 5 molecules as indicated by the balanced equation it would be a second order reaction as.
But the observed rate law suggests that it is a first order reactionT he reaction is a complex reaction and proceeds by two or more successive steps. The resulting carbocation undergoes a rearrangement before proceeding with the alkylation reaction. This is an example of an oxidation reaction.
The mechanism of a chemical reaction is the sequence of actual events that take place as reactant molecules are converted into products. Another example of a synthesis reaction is the formation of potassium. Direct Combination or Synthesis Reaction.
Addition reactions of alkenes will have specific stereochemistry in the finished product. The rate of nucleophilic substitution reactions not only depends on nucleophiles and leaving capacities but also on the mechanism by which the reaction takes place. Electrons are not always paired however even though this is generally the most stable configuration according to the octet rule.
An elementary termolecular reaction involves the simultaneous collision of three atoms molecules or ions. This is the S N 2 mechanism. In addition reactions two atoms are added to a double or triple bond reducing it to a single or double bond.
The combination of iron and sulfur to form iron II sulfide is an example of a synthesis reaction. The Sandmeyer reaction follows a free radical mechanism. Enough energy is present in the system for the same process to occur with the products.
8 Fe S 8 8 FeS. A chemical reaction usually occurs in steps although it may not always be obvious to an observer. Rate kN 2 O 5 2.
It is called substitution nucleophilic bimolecular mechanism. The Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction proceeds via a three-step mechanism. Rate of reaction kN 2 O 5.
This leads to the formation of a charge separated and dipolar intermediate called a betaine. Interestingly the nucleophile can be a. In the simplest synthesis reactions two elements combine to form a binary compound a compound made of two elements.
I need to describe the reaction mechanism using two or less sentences per each step of the mechanism. Involving a single molecule. Referring to the number of individual molecules involved in an elementary step of a reaction mechanism.
2 NO 2 NO 3 NO slow NO 3 CO NO 2 CO 2 fast Each step is called an elementary step and each has its own rate law and molecularity. An atom or molecule that contains one or more unpaired electrons is called a free radical or simply a radical. Alex DowdenEyeEm Getty Images.
Over time iron develops a red flaky coating called rust. In a reversible reaction reacting molecules in a closed system collide with each other and use the energy to break chemical bonds and form new products. Depending on the condition two types of mechanisms have been suggested for performing the Wurtz reaction.
It follows 2 nd order kinetics and the rate. When two substances which by their action upon each other develop much heat enter into reaction the reaction is usually complete without the employment of an excess of either. A possible mechanism for the overall reaction that explains the rate law is.
Here is the chemical equation for the rusting of iron. Step 1 N 2 O 5. Synthesis Reaction Examples.
In a synthesis reaction two or more chemical species combine to form a more complex product. By a formation of free radicals as an intermediate. The Vapour phase is considered a suitable phase for free radicals.
8 Fe S 8 8 FeS. The combination of iron and sulfur to form iron II sulfide is an example of a synthesis reaction. Termolecular elementary reactions are uncommon because the probability of three particles colliding simultaneously is less than one one-thousandth of the probability of two particles colliding.
Other everyday examples include formation of verdigris on copper and tarnishing of silver. One in which the nucleophilic attack and the loss of the leaving group happen at the same time and the second in which the loss of the leaving group happens before the nucleophile can attack. A B AB.
There are two mechanisms proposed for nucleophilic substation reactions. The reaction is actually a two-step process where the synthesis of aryl halides from primary aryl amines involves the formation of diazonium salts and the transformation of diazo intermediates into aryl halides displacement with a nucleophile. Describe reaction mechanisms for chlorination of methane and for polymerization using free radicals.
The elementary steps should add up to the original reaction. For example when a mixture of hydrogen and oxygen in the proportions to form water 2E120 20H2 is exploded it is entirely converted into water. The reaction mechanism or reaction path is the process or pathway by which a reaction occurs.
These reactions are divided in two main types. The Wittig reaction mechanism proceeds via three steps. The decomposition of ozone for example appears to follow a.

Gabriel Phthalimide Synthesis Mechanism Explanation And Examples
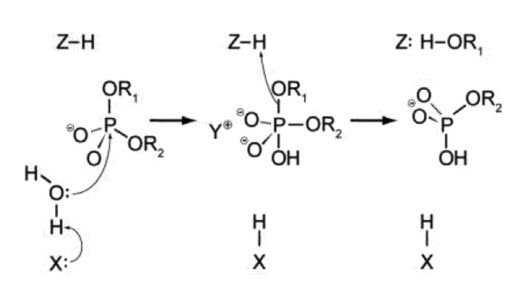
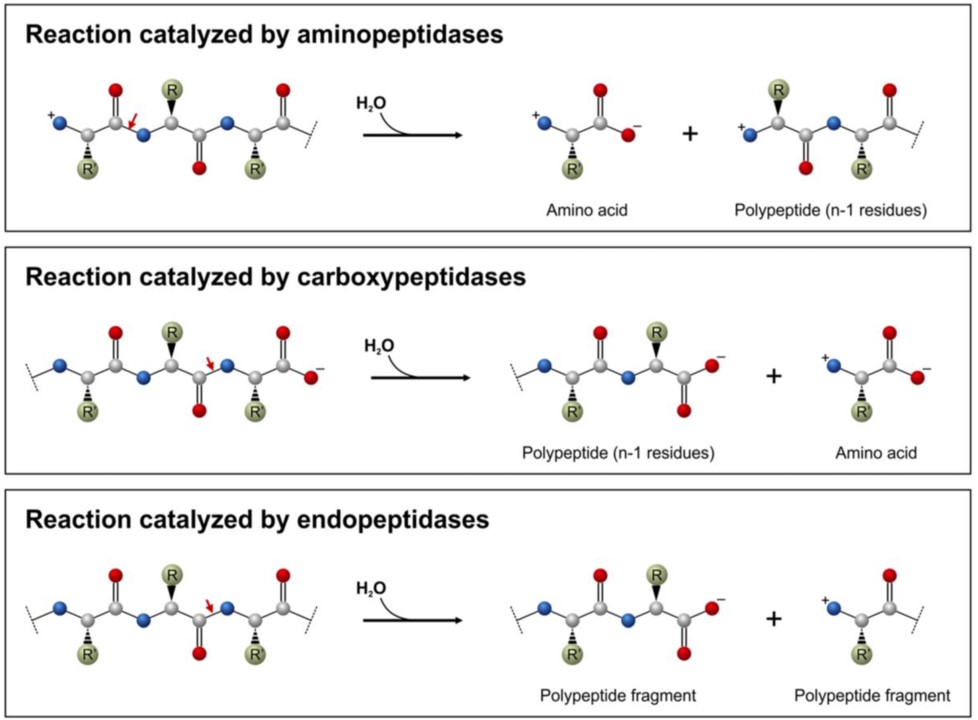
Chapter 7 Catalytic Mechanisms Of Enzymes Chemistry

Chapter 7 Catalytic Mechanisms Of Enzymes Chemistry

Addition Polymerization An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
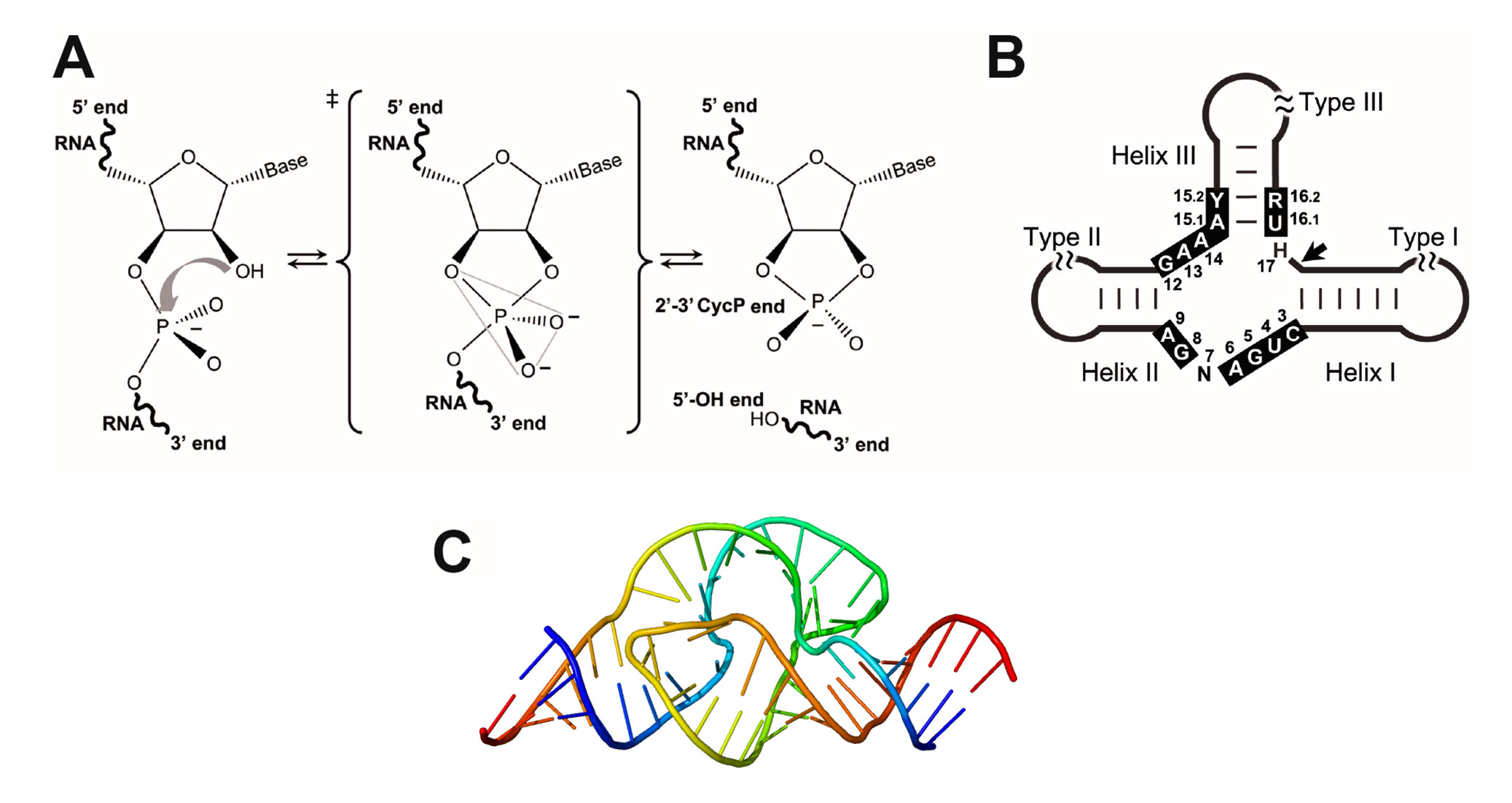
Chapter 7 Catalytic Mechanisms Of Enzymes Chemistry
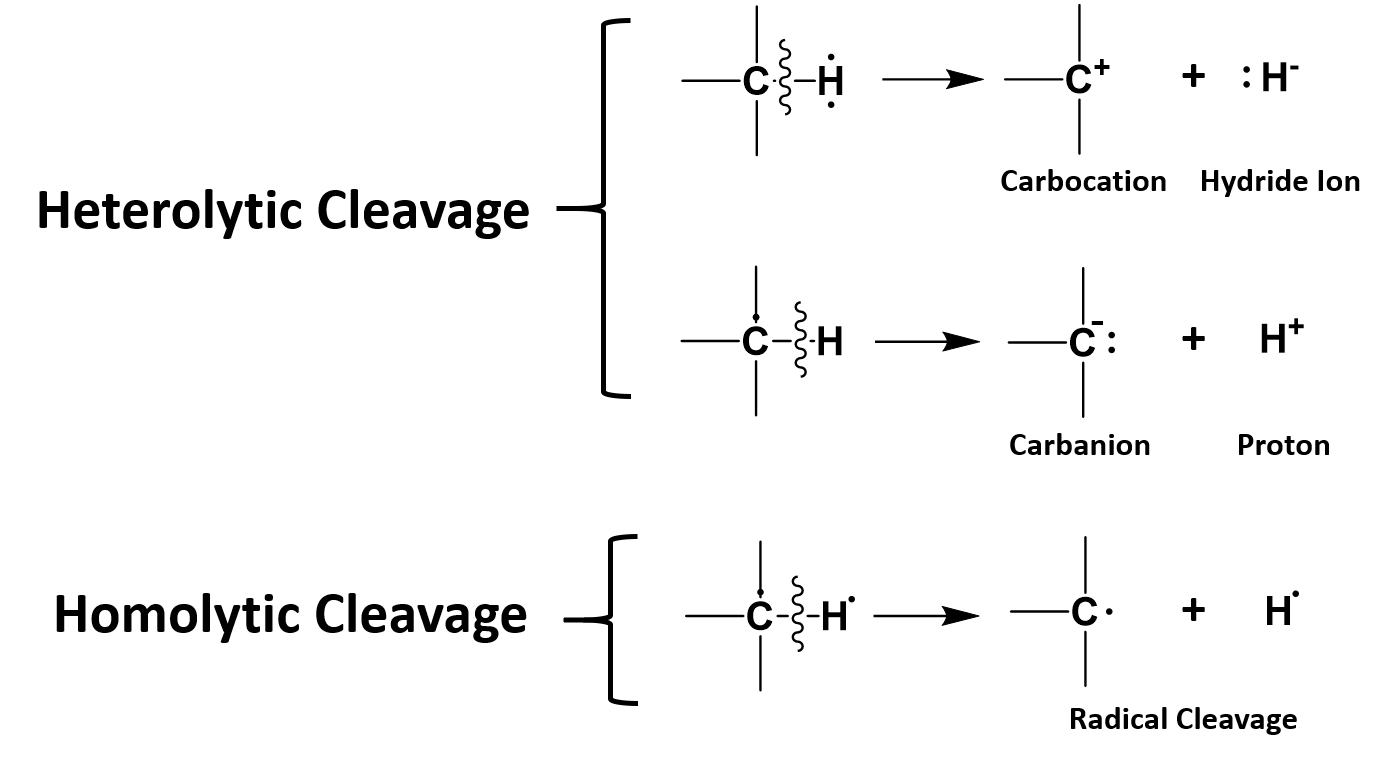
Chapter 7 Catalytic Mechanisms Of Enzymes Chemistry

Mcb Exam 4 Sapling Flashcards Quizlet
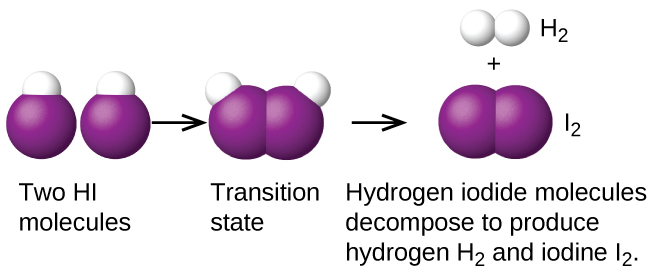
12 6 Reaction Mechanisms Chemistry
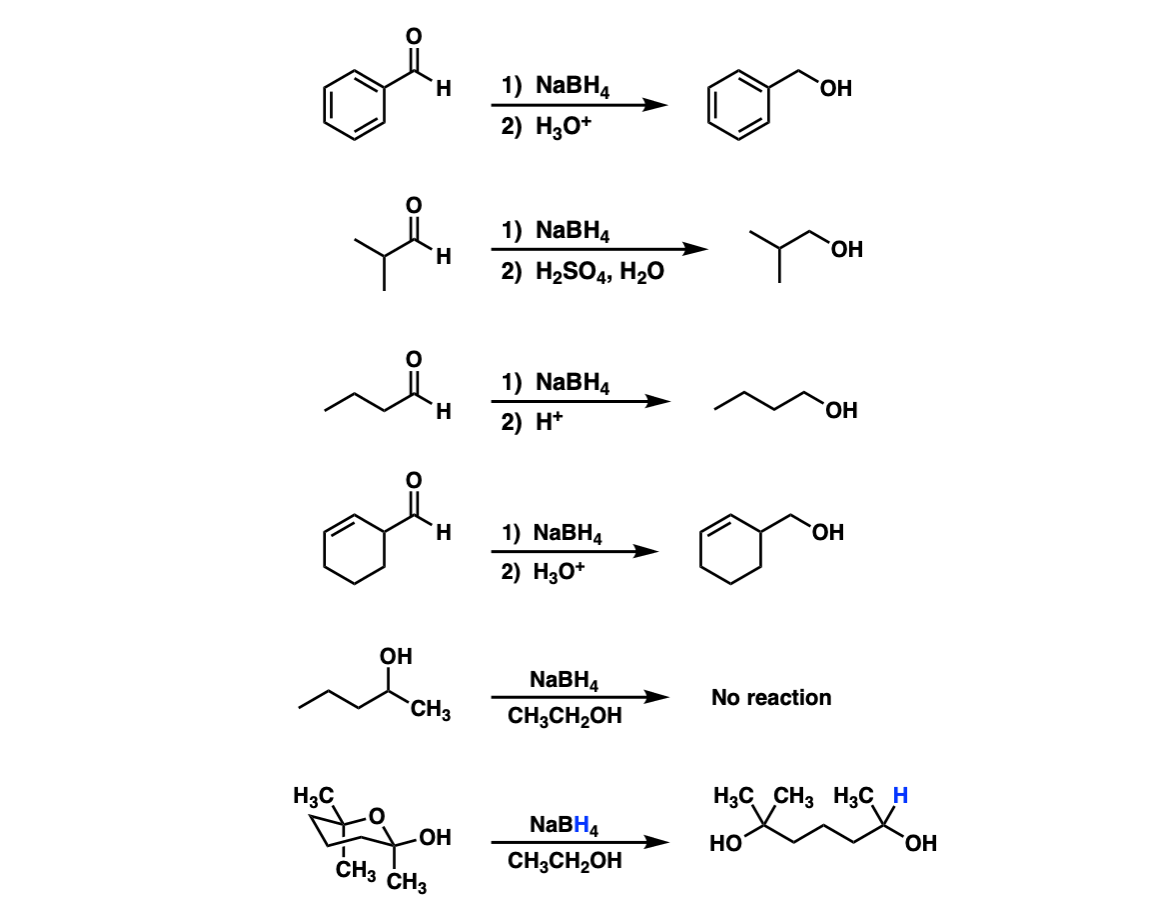
Addition Of Nabh4 To Aldehydes To Give Primary Alcohols Master Organic Chemistry

Addition Polymerization An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
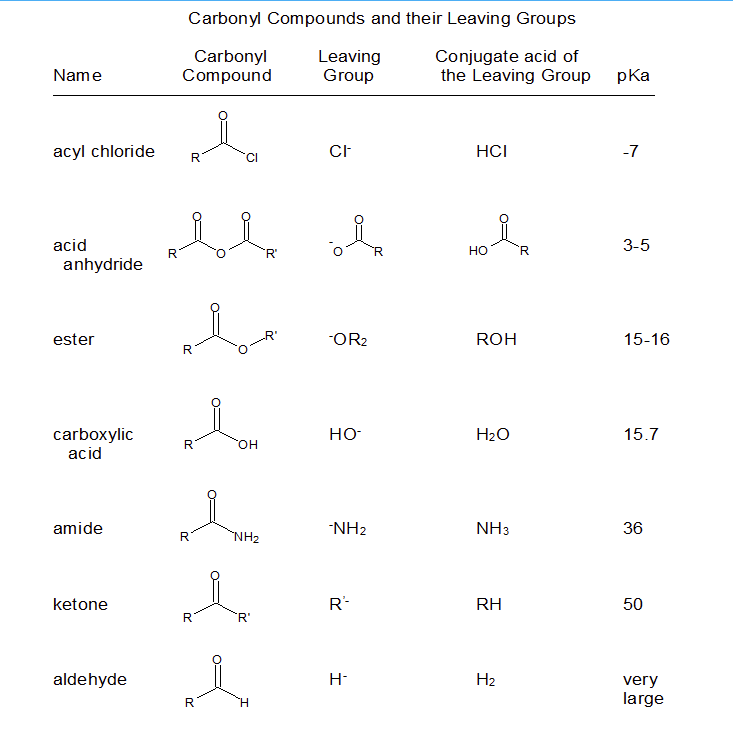
21 2 Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions Chemistry Libretexts

Lithium Aluminum Hydride Lialh4 Reduction Reaction Mechanism Youtube